Translate this page into:
Onychomadesis following hand foot and mouth disease
*Corresponding author: Anupam Das, Department of Dermatology, Kali Pradip Chaudhuri Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata 700032, West Bengal, India. anupamdasdr@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Chatterjee S, Das A. Onychomadesis following hand foot and mouth disease. J Onychol Nail Surg. doi: 10.25259/JONS_29_2024
CASE DETAILS
An 11-year-old boy presented with an altered appearance of fingernails. Examination showed proximal splitting of the nail plate from nail bed along with shedding of the nails of the index and middle fingers of the left hand [Figure 1]. Similar changes were seen in the middle finger nail of the right hand as well. There was a history of an episode of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) 5 weeks ago. A diagnosis of onychomadesis was made, and the parents were informed regarding the self-limiting nature of the nail changes.
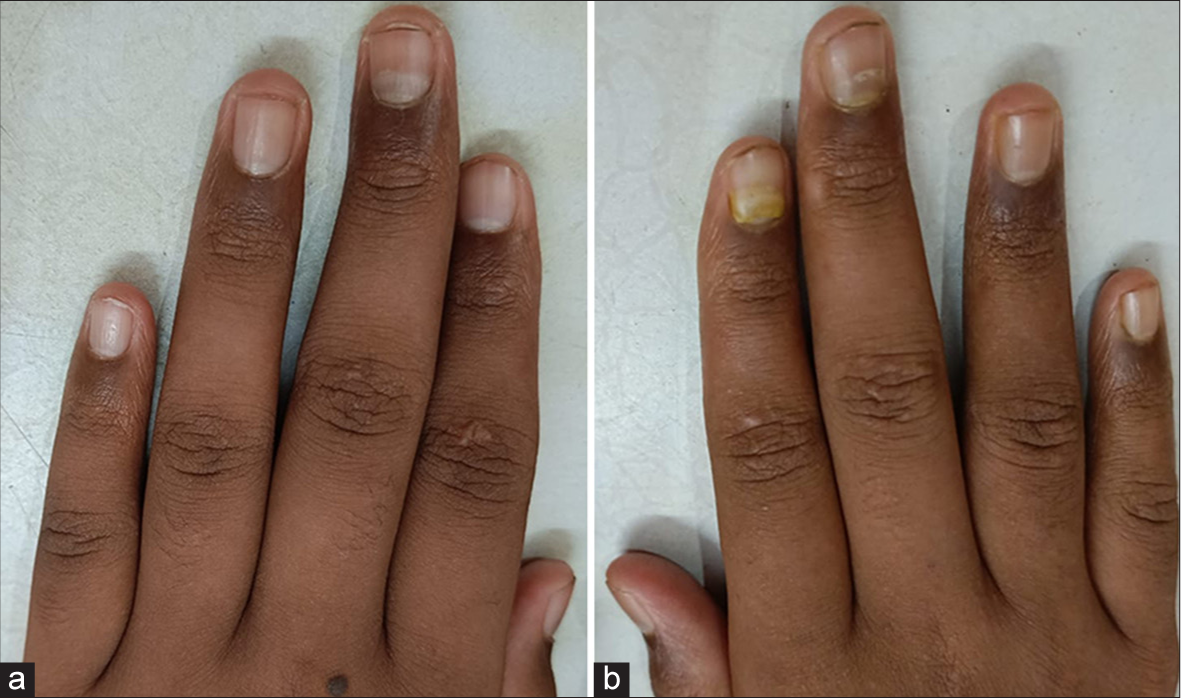
- Clinical image showing onychomadesis involving the index and middle finger of the (a) left hand and (b) middle finger of the right hand.
DESCRIPTION
Onychomadesis refers to the separation of the nail plate from the proximal nail fold due to a number of causes including viral infections (HFMD), autoimmune diseases, drugs (anti-cancer drugs, antibiotics such as azithromycin, penicillins, systemic retinoids and anti-epileptic drugs), systemic diseases (immunodeficiency syndromes, Kawasaki disease), and trauma. However, many cases are idiopathic. Fingernails are found to be more commonly involved. The exact pathomechanism is not known; however, it is postulated that both onychomadesis and Beau’s lines belong to the same spectrum of onychodystrophies developing as sequelae to the temporary arrest of the growth of nail matrix, with onychomadesis belonging to the severe end of the spectrum. In general, treatment is not needed with spontaneous resolution within 1–2 months is the rule.
Authors contributions
Both authors contributed to the manuscript preparation, acquisition of data, analysis, interpretation of data, drafting the article and revising it clinically for important intellectual content and final approval of the submitted version.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship: Nil.







